How to Record 3D Audio: A Full Guide
Recording 3D audio can be a considerable challenge, a struggle many people in the field encounter. Having personally faced the hardships of creating these audio recordings, I understand the frustration involved.
There are multiple ways that you can record 3D audio, and two ways I have done this have been through binaural technology and ambisonic recordings; these are the two most used methods for recording binaural audio and 3D sound, which often prove to be the most successful ways of doing it.
In this article, we're going to take a look at some of the ways you can record 3D audio, what tools you would need to record, and how to use software like Audiocube to make 3D audio without needing any expensive recoridng gear.
In This Article
3D audio is a type of audio that, when listening, sounds like it's coming from all around you.
You will find out some of the tools you need to record 3D audio.
I will show you how you can make 3D audio without needing to record it.
Audiocube will help with creating 3D audio in a new and exciting way.
What is 3D Audio?
Download Audiocube Now!
3D audio is sound that’s designed to feel like it’s coming from all around you. Unlike traditional stereo, which is limited to two channels, 3D audio creates a sense of depth, distance, and direction. It tricks the human ears (and brain) into believing you're inside a space, not just listening to something from speakers or headphones; it gives the natural experience of human hearing.
I like to think of 3D audio as a way to sculpt sound in space or a room. It’s not just louder or clearer; it’s more immersive. This kind of sound is used in VR, gaming, film, and increasingly in music production. Whether you're walking through a forest in a video game or listening to a live performance recording that feels like you’re in the crowd, 3D audio brings a whole new level of realism and emotion.
There are different technologies behind it, binaural recording, higher-order ambisonics, spatial audio, and multichannel surround, but they all share the same goal: placing sound around the listener in a natural and believable way. If you’ve ever used headphones and thought, “Wow, that sound felt like it came from behind me,” chances are you’ve already experienced a form of 3D audio.
How to Record 3D Audio
When I first started recording 3D audio, the biggest question I had was: what do I actually need to capture immersive sound?
The good news is, you don’t need a high-end studio setup to get started, but there are a few essential tools that make all the difference. It's important to note although similar, this is not the same as stereo recording and is more specific to 3D audio.
What You Need To Record 3D Audio
Here are some of the tools you can use to record 3D audio.
A Binaural Microphone: These are specially designed to mimic the shape and spacing of a human head (both right and left ears), not to be confused with a stereo microphone. Some are shaped like a dummy head with microphones in the ear canals to pick up binaural sound, others are small in-ear mics you can wear. You can use two shotgun mics with good placement, but this makes it much harder.
An Audio Recorder: You’ll need a recorder with at least two inputs and good-quality preamps. If you’re using a USB binaural mic, you can plug straight into your computer, but for field recording or better control, something like a Zoom H4n or Sound Devices MixPre is ideal.
Headphones: Monitoring in real-time helps you understand how spatial your recording sounds. Closed-back headphones give the best isolation while recording, and you can use standard stereo headphones for this. I always double-check playback in the same headphones I expect my audience to use; that’s usually the best way to catch any issues.
A Quiet Environment: Because 3D audio captures so much detail, background noise becomes much more noticeable, and it is highly recommended to use a suitable recording space. Try to record in quiet places or use sound blankets to reduce reflections indoors.
Software for Spatial Audio: If you want to do more than just capture reality, say, reposition sounds, mix elements, or add motion, using spatial audio software is essential. I personally use Audiocube, my own standalone tool, which lets me sculpt 3D soundscapes in a visual, intuitive way.
Optional but useful:
Ambisonic Microphones: If you’re planning on doing post-production spatial mixing, an ambisonic mic like the Zoom H3-VR or Sennheiser AMBEO lets you record a full 360-degree soundfield that can be decoded and manipulated later.
How to Record 3D Audio: A Step-By-Step Guide
Although it sounds quite complex, recording 3D audio can be simple if you know what you're doing. Here is a quick and easy guide to recording 3D audio for yourself:
Step 1: Get a Binaural Mic - Acquire a binaural microphone that captures sound just like human ears.
Step 2: Position Your Gear - Place the microphone in the center of the sound environment. Connect it to a stereo audio recorder.
Step 3: Set Levels & Monitor - Adjust your recorder’s levels to avoid distortion. Plug in headphones to monitor the live 3D sound.
Step 4: Record - Once you are happy with the sound, press record. The final track creates an immersive experience when heard through any headphones.
Once you’ve got these basics, you’re ready to start recording and exploring the world in a three-dimensional format.
Why You Don't Actually Need Equipment to Record 3D Audio
Make 3D Music Without Recording. Download Audiocube.
Here’s something I learned pretty quickly: you don’t have to record 3D audio to create it.
While binaural and ambisonic mics are powerful, especially for capturing real-world ambiance like ASMR videos, they have downsides; recordings are fixed, can be noisy, and offer little post-production control.
I have previously run into setbacks when recording with two microphones separatel. The main issue being phasing issues during the recording from different sound sources, which create problems when listening back to it.
Instead, you can create immersive soundscapes entirely inside your computer with the right software. Tools like Audiocube let you take any mono or stereo sound, a voice, a synth, or a sample, and position it in 3D space. You gain freedom to automate its movement, add additional production to the sound, such as post-processing techniques like compression or equalization, and be more creative with the sounds you are creating.
This modern approach offers more control and flexibility than traditional recording, meaning you can binaurally process any sound within your computer.
Why not give it a go yourself? Download Audiocube for free, or you can buy the full license for all the features.
How to Create 3D Audio with Audiocube - No Microphones Needed
Making 3D audio might sound complicated, but with Audiocube, it’s actually really fun and easy. You can start mixing spatial audio in a flash - and you don’t even need
Here’s how I do it:
Try For Yourself! Download Audiocube.
Download Audiocube - Get started for free, or buy the full version to get access to all the features.
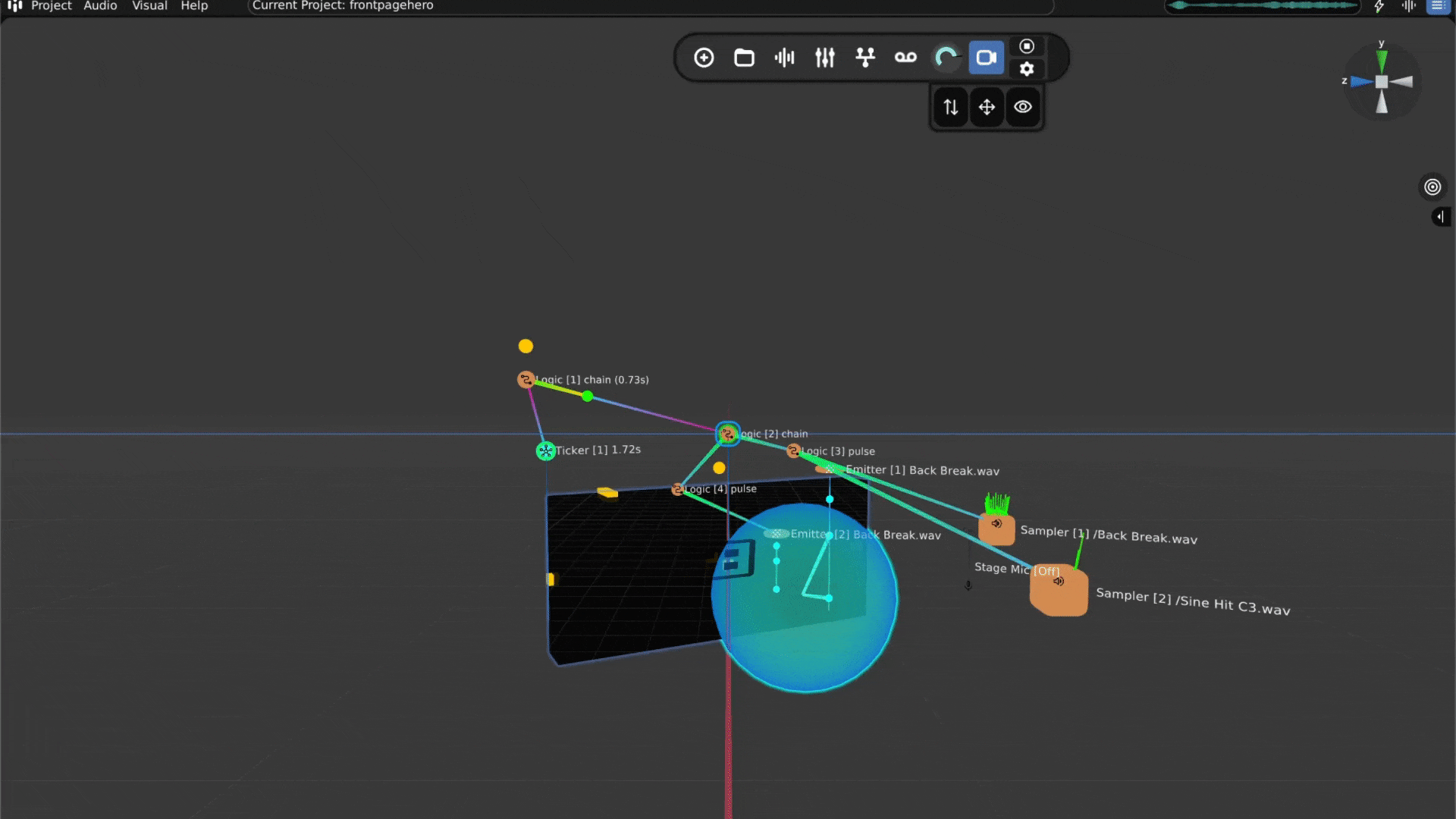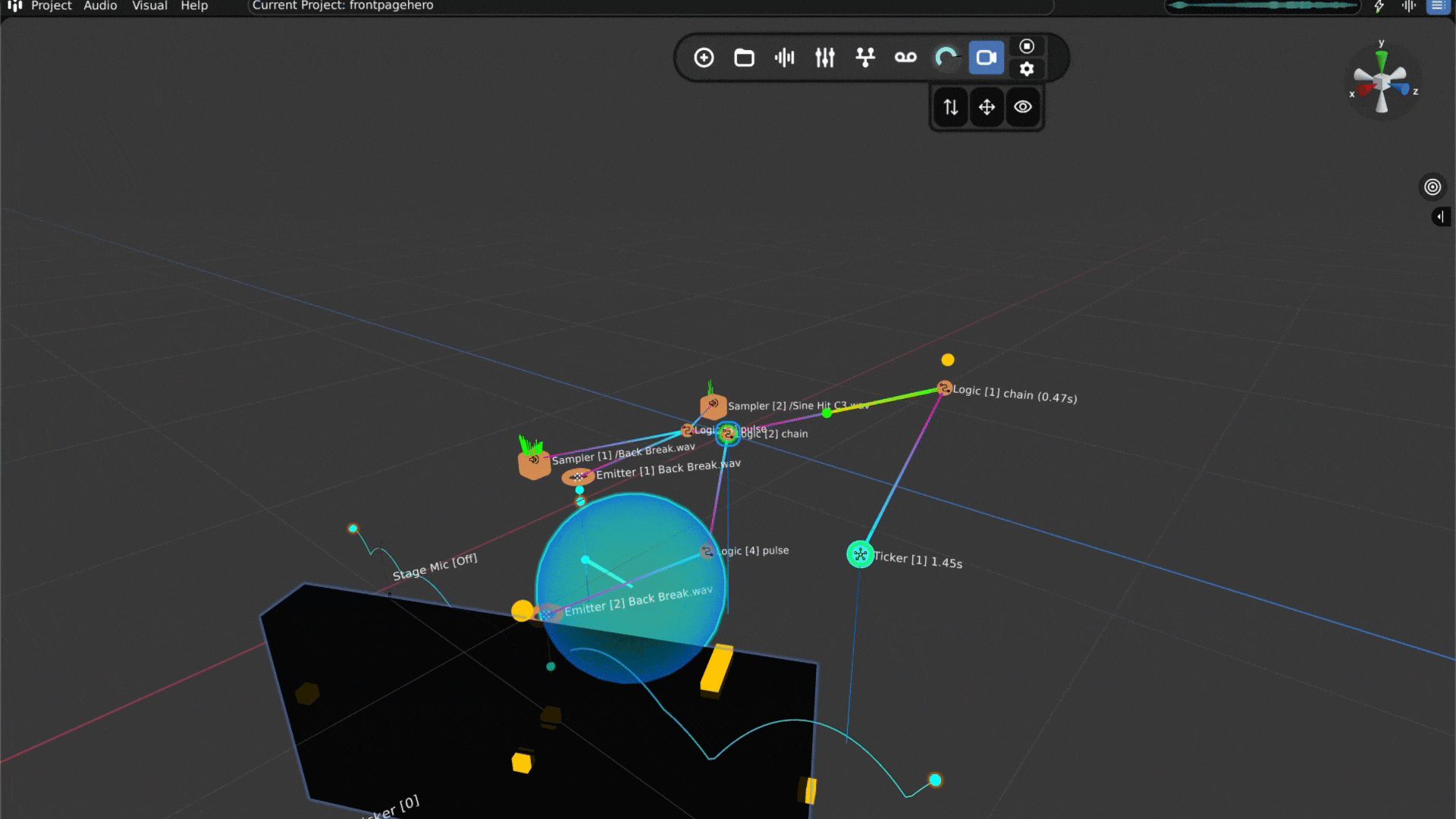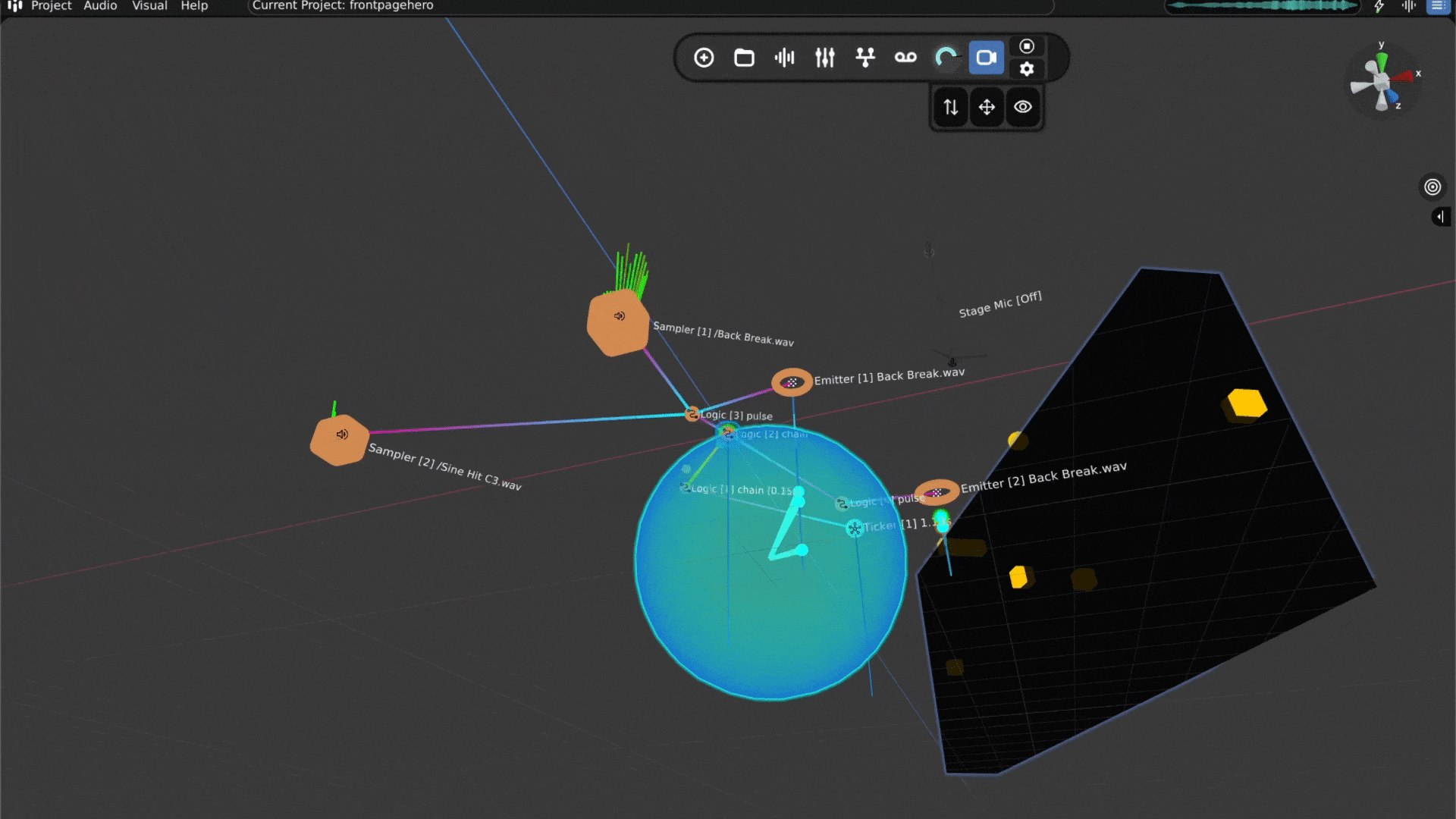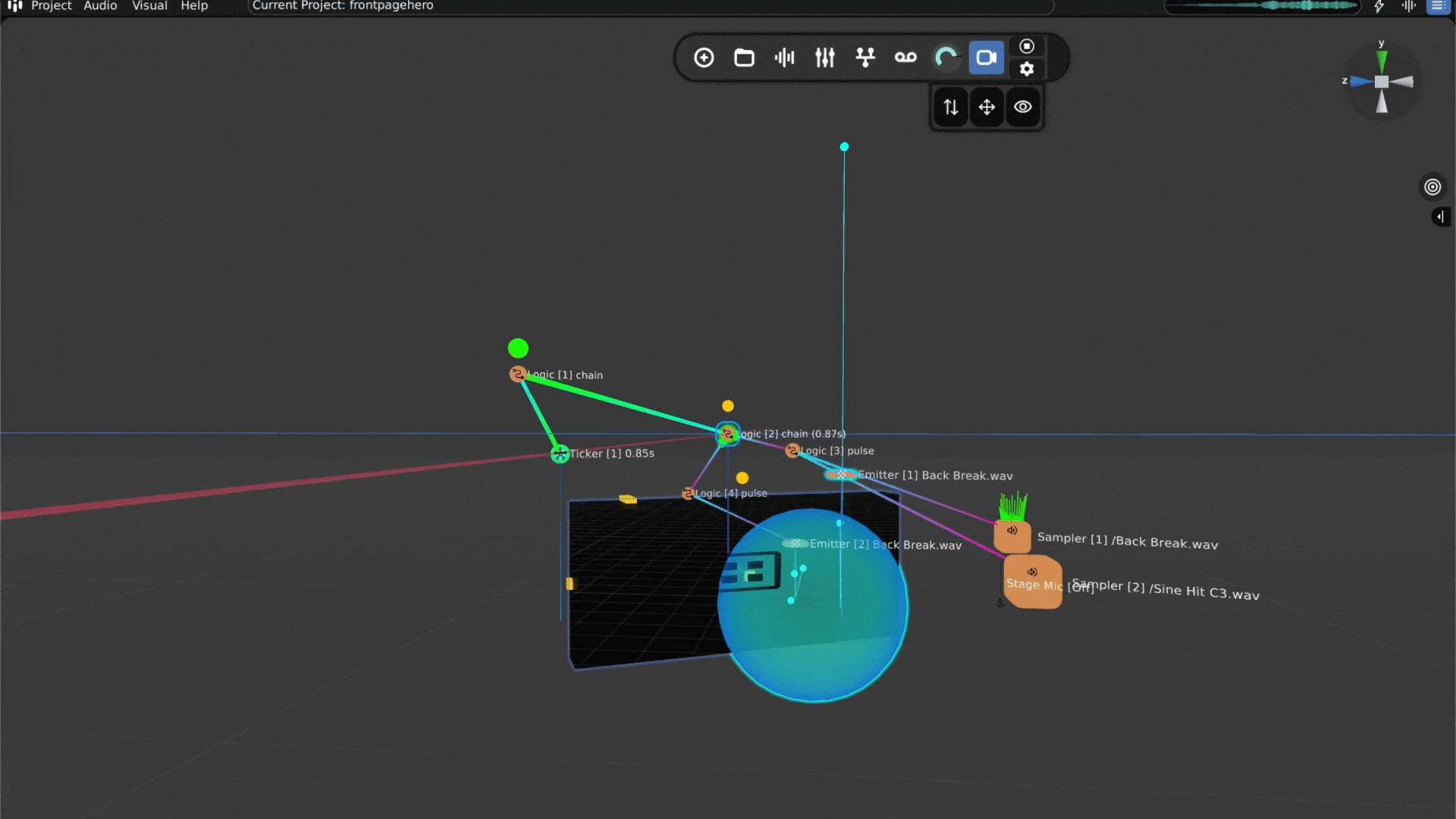
Open Audiocube and Start a New Project - When you open Audiocube, click New Project. You’ll see a 3D grid space; this is where your sounds will live and move.
Add Your Sounds - You can easily import your own files, or use the built-in sample pack downloader with over 2GB of HD, custom samples.
Create a Sampler - Click to add a sampler. This is a virtual object that plays your sound. Choose one of your audio files to play.
Place the Sound in 3D - Move the sampler around in the 3D space to choose where the sound comes from, left, right, behind, above, wherever you want.
Make It Move (Optional) - If you want your sound to move, you can animate it. For example, you can make it spin around the listener or pass from side to side.
Mix and Add Effects – Audiocube comes with a full mixing system. Add reverb, EQ, distortion, and more. You can apply effects to individual devices or shape the overall sound on the master channel.
Tweak the Acoustics – The built-in acoustic engine simulates natural sound behavior, like reflections from boundaries, muffling through walls, and distance fade. You can even activate the head-related transfer functions (HRTF) Binauralizer for a headphone-friendly 360° experience.
Adjust the Mix - Make sure all your sounds blend well together. You can change the volume and position of each sound to get the balance just right.
Export Your 3D Sound - When you’re done, you can export your mix as a WAV file.
It's as easy as that. If you want to try Audiocube for yourself, you can download it for free or purchase a lifetime license to get access to all of its features.
Start Making 3D Audio Without Needing to Record
So there you have it, you now know the different ways for recording spatial audio. There are positives and negatives, and it is important to remember that the recording environment, along with the equipment within it, makes a difference.
Recording 3D audio can be hard, but luckily, with software like Audiocube, you can create 3D sound with just a few clicks on your laptop.
Why not give Audiocube today and start creating your own 3D music? You can download it for free or buy your own lifetime license so you can access all of the features
FAQs about Recording 3D Audio
-
3D audio is recorded using special microphones that capture sound from multiple directions, like binaural or ambisonic audio mics. These mimic how our ears hear sound in space. If you don’t have these mics, you can still create 3D audio in Audiocube by placing regular sounds into a 3D virtual environment.
-
Absolutely, spatial audio is worth it because it transforms flat audio into a captivating 3D experience, adding incredible depth and realism to music, films, and gaming. With interactive tools like Audiocube, creators can easily design these immersive soundscapes, making professional-quality spatial audio more accessible than ever before.
-
Yes, spatial audio and 3D audio are very similar. Both create the feeling that sound is coming from all around you, not just from two speakers. They help make audio more lifelike. Audiocube uses spatial audio tools to let you build 3D sound scenes easily, with simple controls and visual placement.